What is quantitative easing and how does it affect crypto markets?
article by CryptoJelleNL
Monetary policy has taken a step into the spotlights lately, with many crypto traders paying attention to what Jerome Powell and Janet Yellen have to say. In today's article, we tap into this newfound attention and dive into one of the major monetary policy tools: Quantitative easing. Read on to learn more about the tool, how it works, and how it affects crypto markets.
Over the past years, central banks have had a tough battle to fight. The side-effects of a pandemic, raging inflation and to make matters worse: a recession. In their fight, Quantitative easing played a major role. So what is quantitative easing?
What is quantitative easing?
Quantitative easing is a division of monetary policy aimed at increasing the amount of capital (the money supply) in an economy. While each central bank has a slightly different approach, it generally boils down to large-scale purchases of government bonds and securities, or directly lending capital to the market.
As said, the goal of quantitative easing is to push new money into the economy, which boosts economic activity and reduces interest rates, which in turn encourages consumer spending. Therefore, QE is generally considered to be an expansionary monetary policy.
How does quantitative easing work?
Generally speaking, QE works as follows. The Federal Reserve, or European Central Bank buys bonds from commercial banks, which pushes bond prices higher, and provides banks with more capital to lend out to its customers.
As a result of the higher bond prices, and the new capital available to the banks, interest rates fall. Lower interest rates encourage borrowing and discourage saving - providing a significant boost to consumption and investment. Generally speaking, it results in new jobs too.
Why is quantitative easing used?
In most cases, Quantitative easing is used as a last resort. Central Banks usually boost the economy by decreasing the short-term interest rate; but when this interest rate is already at zero, further decreases are not very effective.
In these cases, or when the situation calls for extreme intervention, central banks often opt for QE programs. This most notably happened in the aftermath of the 2007 financial crisis, where the European Central Bank, the Bank of England, and the Federal Reserve all resorted to billions of direct lending and asset purchases.
Risks of quantitative easing
Quantitative easing is not without risks, though. One of the most commonly known drawbacks of QE is that its use can result in surging inflation, which can hurt the economy down the line. Therefore, central banks need to navigate the fine line between boosting the economy and causing excessive inflation carefully. There is a lot of disagreement on whether the benefits of QE outweigh the inflationary downsides.
Some economists argue that QE is kicking the can down the road, where businesses are kept afloat so long as QE is active, and the house of cards comes crashing down when the music stops.
Quantitative easing and inflation in a post-pandemic world
While central banks traditionally use their reserves to operate quantitative easing programs - we have seen a change of approach in the most recent quantitative easing programs of 2020 and 2021. Instead of just moving funds around, central banks have resorted to creating money out of thin air; resulting in a boatload of money printer memes.
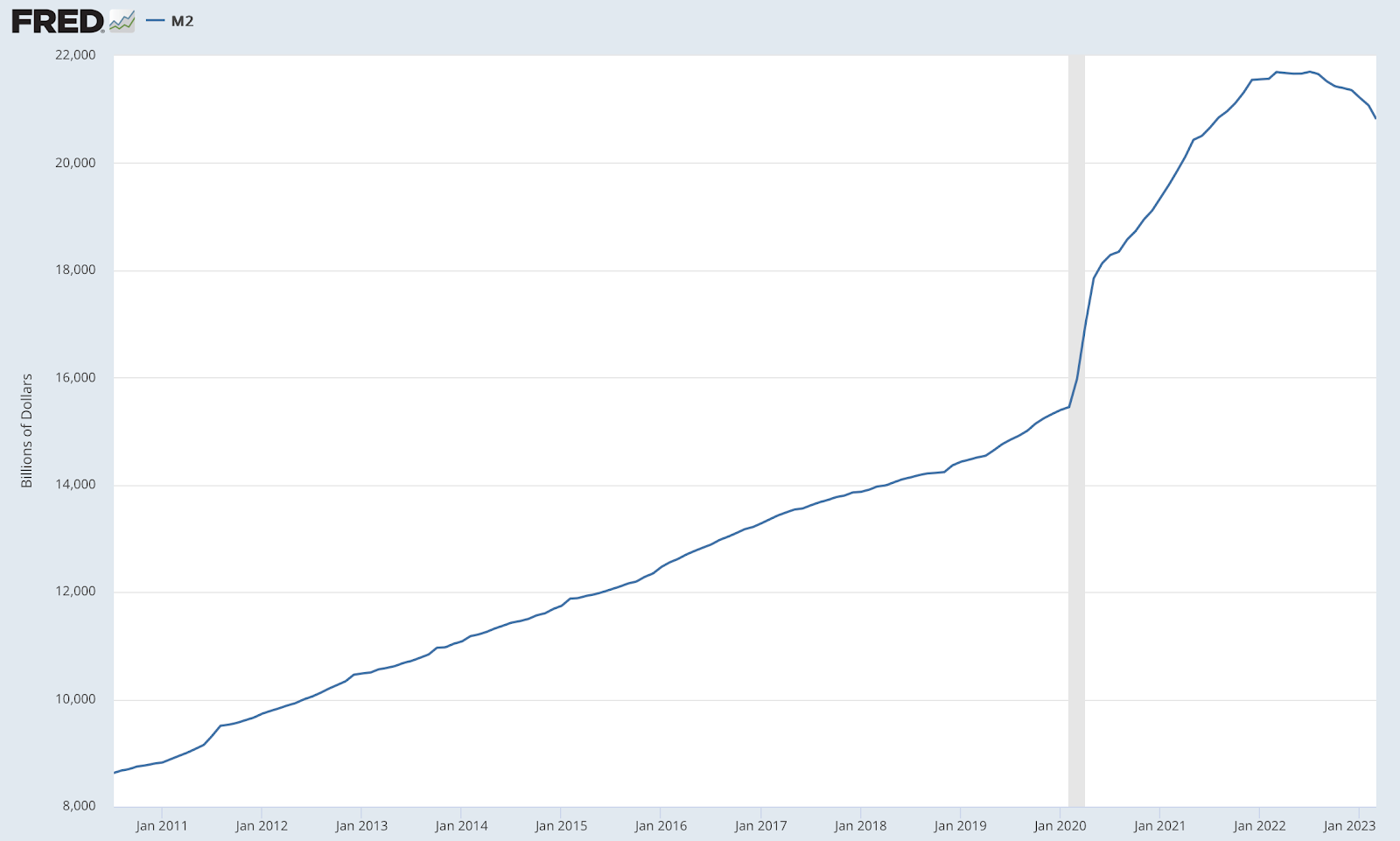
Chart: M2; Total Money Supply in the United States. Note the increase after March 2020.

Fed Chair Jerome Powell operating the money printer
Economists were already worried about the tendency of QE to cause inflation, but the past months have shown that QE powered by money creation causes even bigger problems. Inflation peaked at 9.1% in June 2022, while inflation oscillated between one and two percent before the QE program started.
The Federal Reserve is still actively trying to bring that inflation back down, pushing interest rates from zero to five percent in a little over a year.
Quantitative easing and markets
Even though the Fed is still actively combatting the inflationary effects of QE, there are early signs of new capital injections into the global economy. In the below tweet, CryptoJelleNL highlights how the different central bank balance sheets have slowly started to creep up again, while also noting a correlation between these balance sheets and Bitcoin price action.
BITCOIN AS A HEDGE AGAINST MONEY PRINTERS?
— Jelle (@CryptoJelleNL) May 10, 2023
The below chart shows the global central bank balance sheets (in black) and the price of Bitcoin (in red).
Governments are starting to grow the balance sheets again.#Bitcoin will follow suit; expecting higher prices. pic.twitter.com/njR4QMGu3Y
This phenomenon was widely observed in equity markets as well, where the stock market started a year-long rally just days after the ECB and Federal Reserve both announced massive QE packages in the third week of March.
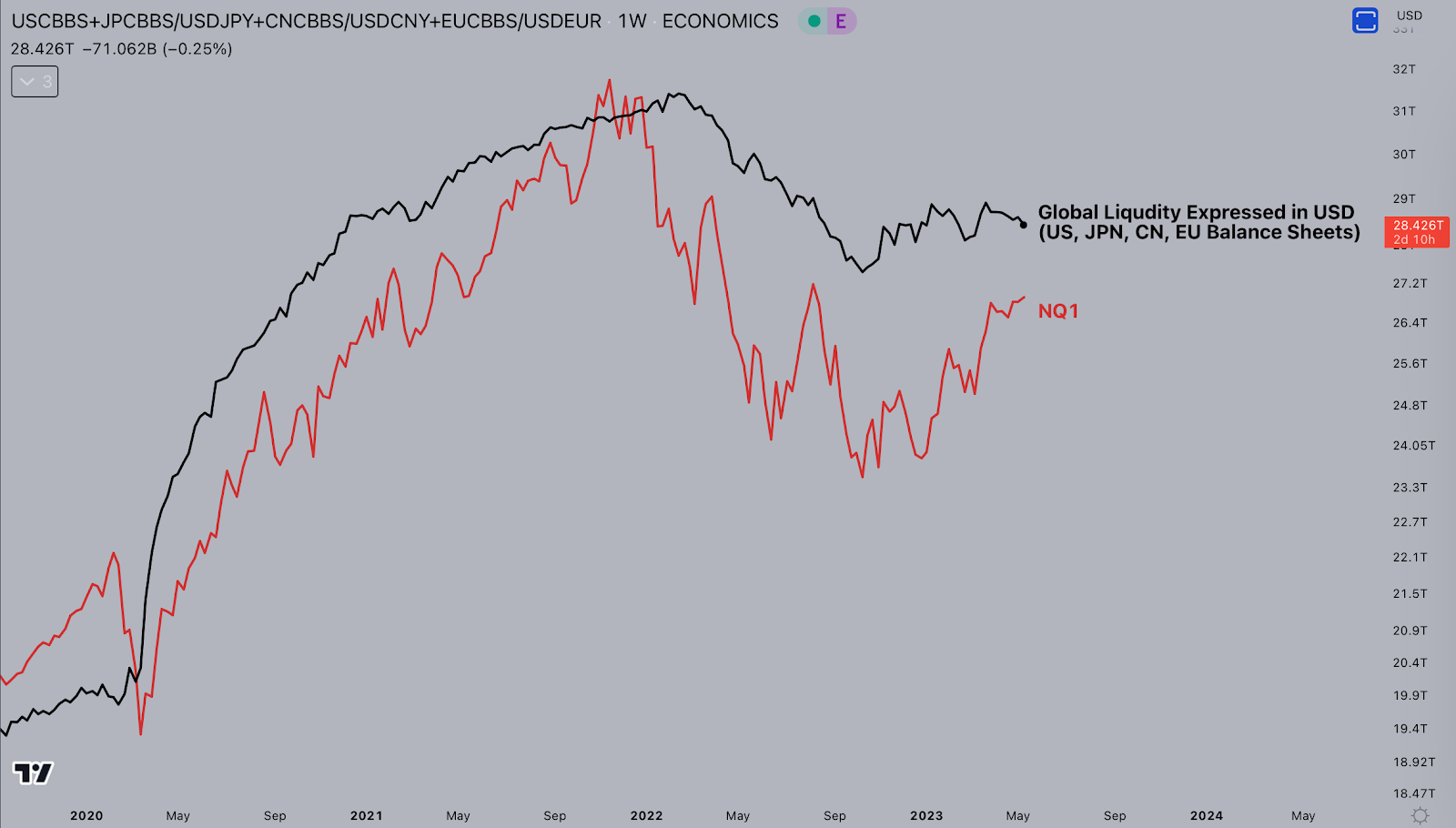
As you can see, the Nasdaq 100 peaked just weeks before the end of QE programs across the world, coming down just as fast as it came up. All in all, global markets seem to be closely correlated to global liquidity conditions.
This solidifies the idea of Bitcoin and stocks as a hedge against inflation. Money supply increases have been shown to cause inflation and push up the markets, whereas a contraction in money supply pushes the market back down, and also curbs inflation to a degree.
What is next?
Because of the clear correlation between global liquidity and asset prices, many institutions and traders are trying to predict the next moves of central banks, however difficult this might be.
As it stands, China has announced smaller-scale capital injections ($92 billion of reverse repurchase contracts in February 2023, for example), and the economic situation in the United States may soon call for a new expansionary policy as well.
Closing thoughts
To summarise, quantitative easing is a program used by central banks to boost the economy, when lowering interest rates can no longer make a difference. With QE, governments purchase bonds on a large scale or directly lend money to the banks.
In recent years, governments artificially created money to support these programs, instead of using the central bank reserves, which has resulted in steep inflation across the globe.
Quantitative easing also seems to affect global markets, with the most recent campaign triggering a relentless bull run in various asset classes, which ended just weeks before the end of the QE campaigns.
Predicting the next move of central banks is incredibly difficult, and probably above most of our pay grades. Nevertheless, studying the driving forces behind economies is a worthwhile activity that will help you understand why markets move the way they do.
Author's Disclaimer: This article is based on my limited knowledge and experience. It has been written for informational purposes only. It should not be construed as investment advice in any shape or form.
Editor's note: CryptoJelleNL provides insights into the cryptocurrency industry. He has been actively participating in financial markets for over 5 years, primarily focusing on long-term investments in both the stock market and crypto. While he watches the returns of those investments roll in, he writes articles for multiple platforms. From now on, he will be contributing his insights for Alpha Circle as well.
Check out his twitter: twitter.com/cryptojellenl
—
The content above is neither a recommendation for investment and trading strategies nor does it constitute an investment offer, solicitation, or recommendation of any product or service. The content is for informational sharing purposes only. Anyone who makes or changes the investment decision based on the content shall undertake the result or loss by himself/herself.
The content of this document has been translated into different languages and shared throughout different platforms. In case of any discrepancy or inconsistency between different posts caused by mistranslations, the English version on our official website shall prevail.


